Solar magnetic polarity effect on neutron monitor count rates from latitude surveys versus Antarctic stations
-
63 views
-
2 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 5, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 16. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://icrc2021.desy.de/pf_access_abstracts
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/Presenter-Forum-1-Evening-All-Categories/48
Abstract:
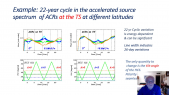
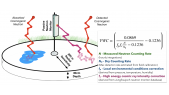
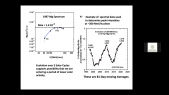
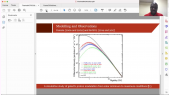
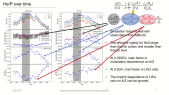
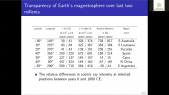
'The Galactic cosmic ray spectrum manifests subtle variations over the 22-year solar magnetic cycle in addition to more pronounced variations over the 11-year sunspot cycle. We conducted numerous latitude surveys by operating a neutron monitor onboard an icebreaker that traveled across a wide range of geomagnetic cutoff rigidities. Here we revisit our previous work to study spectral changes using 13 annual latitude surveys from 1994 to 2007 by comparing with neutron monitor data from Mawson instead of McMurdo, which closed in 2017, in order to allow a comparison with more recent latitude surveys. We confirm linear trends between count rates at different geomagnetic cutoff rigidities and changes in slope before and after the polarity reversal in 2000 as an effect of solar magnetic polarity. We performed two more latitude surveys (in 2019 and 2019-20) with a monitor similar to the 3NM64 in the previous surveys but without lead rings around the central tube, a so-called “semi-leaded neutron monitor.” We also found similar results for the relationship between the count rate of the semi-leaded neutron monitor and that of the Jang Bogo and Mawson neutron monitor stations in Antarctica.'
Authors: Kledsai Poopakun
Co-Authors: Waraporn Nuntiyakul | David Ruffolo | Paul Evenson | Peng Jiang | Pongpichit Chuanraksasat | Marc Duldig | John Humble | Suyeon Oh
Indico-ID: 259
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/1268
Kledsai Poopakun