New neutron monitor altitude-dependent yield function and its application to an analysis of neutron-monitor data
-
95 views
-
2 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 5, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 21. July 2021 - 12:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/24-Ground-based-measurements-of-low-energy-GCRs-SH/98
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-07/8
Abstract:
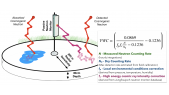
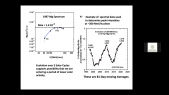
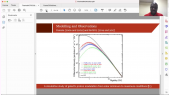
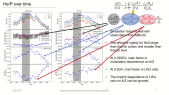
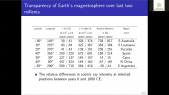
'An updated yield function (YF) of a standard NM64 neutron monitor (NM) is computed and extended to different atmospheric depths from sea level to 500 g/cm$^2$ ($sim$5.7 km altitude) and is presented as lookup tables and a full parametrization. NM YF was computed using the PLANETOCOSMICS simulation tool based on the GEANT4 package, applying the NRLMSISE-00 atmospheric model. The yield function was validated using the cosmic-ray spectra directly measured in space by the AMS-02 experiment during the period May 2011 through May 2017 and confronted with count rates of all NM64-type NMs being in operation during this period. Using this approach, the stability of all the selected NMs was analyzed for the period 2011–2017. Most of NMs appear very stable and suitable for studies of long-term solar modulation of cosmic rays. However, some NMs suffer from instabilities like trends, apparent jumps, or strong seasonal waves in the count rates.'
Authors: Alexander Mishev | Sergey Koldobskiy | Gennady Kovaltsov | Ilya Usoskin
Indico-ID: 364
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/1247
URLs to accompanying publications:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/2019JA027433
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1029/2018JA026340
Sergey Koldobskiy