New empirical methods for correction of meteorological effects on cosmic ray muons
-
110 views
-
0 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 15, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 15. July 2021 - 12:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/22-Atmospheric-effects-of-CR-SH/122
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-07/8
Abstract:
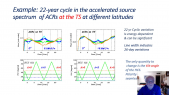
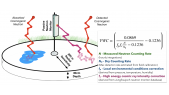
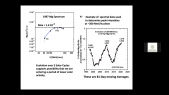
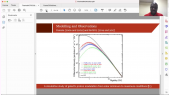
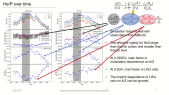
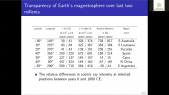
'Flux of muon component of secondary cosmic rays is affected by varying conditions in the atmosphere. Dominant effects are barometric and temperature effect which reflect variations of atmospheric pressure and atmospheric temperature respectively. Precise modeling and correction for these meteorological effects significantly increases sensitivity of Earth-based muon detectors to variations of primary cosmic ray flux. rnWe are presenting two recently developed empirical methods for correction of meteorological effects on cosmic ray muons. First method is based on principal component analysis, while second employs multivariate analysis using machine learning techniques. Both methods are applied for correction of barometric and temperature effects, but can easily be generalized to take more atmospheric parameters into account.rnWe apply these corrections to muon count rates measured by Belgrade cosmic ray station and study their effect on sensitivity of detection of periodic and aperiodic flux variations of primary cosmic rays. Comparison with the most widely used method for correction of meteorological effects – integral method, as well as with neutron monitor data, demonstrates very high effectiveness of presented methods.'
Authors: Mihailo Savic
Indico-ID: 931
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/1252
Mihailo Savic