Periodicities Observed in Neutron Monitor Counting Rates Throughout Solar Cycles 20-24
-
289 views
-
0 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 7, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 14. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/21-Short-term-modulation-SH/117
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-07/8
Abstract:
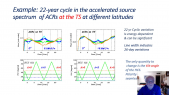
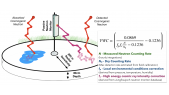
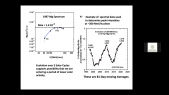
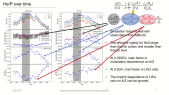
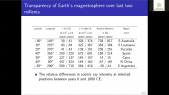
'Neutron monitor cosmic rays and Sun Spot Number (SSN) measurements from 1964 to 2019 corresponding with the Solar Cycles 20–24 have been used. A Global Neutron Monitor (GNM) has been built as virtual representative station to characterize solar activity. Morlet wavelet analysis was applied to the GNM and SSN in order to determine possible periodicities. This analysis was applied both tornthe whole studied interval (1964–2019) and to each Solar Cycle separately. The 27-day period and its second harmonic, related to solar synodic rotation, a periodicity between 45 and 84 days, the Riegerrnperiod and nearly annual period have been detected in all SCs in the two analyzed magnitudes. On a larger scales, 1.3–, 1.7–,11– and 19–year periods were obtained in GNM counting rates and 2.4-, 3.3–, 5.6- and 11-year period in SSN. A time lag analysis between GNM and SSN have also been performed.rnThe result obtained in this study confirms previous works: in the even SCs, the maximum value of cross-correlation function occurs in a lag of 4—6 days while in the odd SCs in a lag of 100—300 days. This fact implies that the modulation of cosmic rays by solar activity is different for odd andrneven cycles.'
Authors: Alejandro López Comazzi
Co-Authors: Juan José Blanco Ávalos
Collaboration: SRG-UAH
Indico-ID: 1180
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/1304
Alejandro López Comazzi