The YAG Lidar System Applied in LHAASO
-
102 views
-
0 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded September 2, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 21. July 2021 - 12:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/92210078166
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 92210078166
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/13-New-Instrumentation-and-Tools-for-EAS-Detection-CRI/92
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-03/4
Abstract:
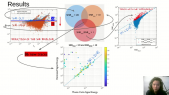
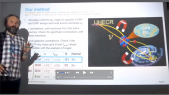
'The atmospheric quality plays an import role in the air shower observation by the Wide Field of View Cherenkov Telescope Array (WFCTA) of LHAASO. A YAG imaging lidar system was developed to continuously monitor the calorimetric information. The accuracy of atmospheric monitoring is dependent on the pulse energy, the YAG laser’s beam parameters and the angular repeatability of a High-precision 3Dxa0lifting Rotating Platform (HiRoP). Therefore, we designed an optical system for this lidar with a beam splitter to divide the laser beam into a reference beam and a calibrating beam with a certain ratio and coupled the beam paths with the movement of HiRoP. Thus, every pulse energy of the calibrating beam, which has the same energy fluctuation with respect to the reference beam recorded by a power meter, could be calculated by the ratio of the two beams. Great cares were also taken to characterize the beam size, polarization and divergence of the laser. Meanwhile, a high-precision home-made thermotank was designed to control the temperature and humidity to improve the performance and stability of our laser system, which resulting in a thermal fluctuation less than 2 0C inside the container in the winter at an altitude of 4410 m. Finally, the pulse energy fluctuation of the calibrating beam was about 1.5%, much less than that of 9% without the thermotank. As a result, we have successfully attained distinguishable full-WFCTA-view scanning Laser images in different air conditions, which could be used for the atmospheric quality analysis in further.'
Authors: Qinning Sun
Co-Authors: Lisi Geng | Xin Li | Junji Xia | Long Chen | Hu Liu | Yang Wang | Fengrong Zhu | Yong Zhang
Collaboration: Lhaaso
Indico-ID: 1281
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/272
Qinning Sun