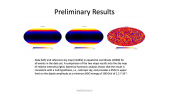
The Plastic Scintillator Detector of the HERD space mission
-
83 views
-
5 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 5, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 16. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://icrc2021.desy.de/pf_access_abstracts
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/Presenter-Forum-1-Evening-All-Categories/48
Abstract:
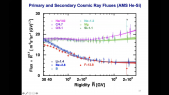
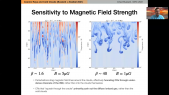
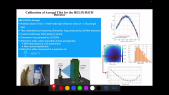
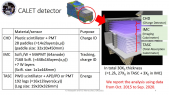
'The High Energy cosmic Radiation Detector (HERD) is one of the prominent space-borne instruments to be installed on board the upcoming Chinese Space Station (CSS) in 2026 and is the result of a collaboration among chinese and european institutions. Primary scientific goals of HERD include: precise measurements of the cosmic ray (CR) energy spectra and mass composition at energies up to few PeV, electron/positron spectra up to tens of TeV, CR anisotropy, gamma ray astronomy and transient studies, along with indirect searches for Dark Matter particles. HERD is configured to accept incident particles from both its top and four lateral sides. Owing to its pioneering design, more than one order of magnitude increase in geometric acceptance is foreseen, with respect to previous and ongoing experiments.rnThe Plastic Scintillator Detector (PSD) constitutes an important sub-detector of HERD, particularly aimed towards photon tagging and precise charge measurements of incoming CR nuclei in a range of Z = 1 - 26. Main requirements concerning its design, include: high detection efficiency, broad dynamic range and good energy/charge resolution. In order to define the optimal layout, two configurations are currently under investigation: one based on long scintillator bars and the other on square tiles, with both layouts being readout by Silicon Photomultipliers (SiPMs). Ongoing activities and future plans regarding the HERD PSD will be presented in this work.'
Authors: Dimitrios Kyratzis | For the HERD Collaboration
Collaboration: HERD
Indico-ID: 214
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/054
Dimitrios Kyratzis