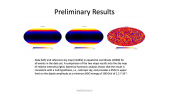
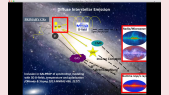
The low rate of supernova remnant pevatrons
-
143 views
-
7 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 3, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 15. July 2021 - 12:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/91896950007
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 91896950007
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/14-CRs-and-ISM-CRD/45
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-06/7
Abstract:
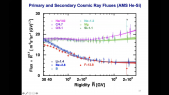
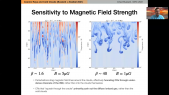
'Although supernova remnants remain the main suspects as sources of Galactic cosmic rays up to the knee, the supernova paradigm still has many loose ends. The weakest point in this construction is the possibility that individual supernova remnants can accelerate particles to the rigidity of the knee, ~ 106 GV. This scenario heavily relies upon the possibility to excite current driven non-resonant hybrid modes while the shock is still at the beginning of the Sedov phase. These modes can enhance the rate of particle scattering thereby leading to potentially very-high maximum energies. Here we calculate the spectrum of particles released into the interstellar medium from the remnants of different types of supernovae. We find that only the remnants of very powerful, rare core-collapse supernova explosions can accelerate light elements such as hydrogen and helium nuclei, to the knee rigidity, and that the local spectrum of cosmic rays directly constrains the rate of such events, if they are also source of PeV cosmic rays. The implications for the overall cosmic ray spectrum observed at the Earth and for the detection of PeVatrons by future gamma-ray observatories are discussed.'
Authors: Elena Amato | Pasquale Blasi | Pierre Cristofari
Indico-ID: 230
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/151
Pierre Cristofari