Gamma-Ray Polarization Results of the POLAR Mission and Future Prospects
-
92 views
-
4 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 5, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 14. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/98542982538
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 98542982538
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/47-The-central-engines-of-fast-transients-Gamma-Ray-Bursts-and-Fast-Radio-Bursts-GAD-GAI-MM/112
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-04/5
Abstract:
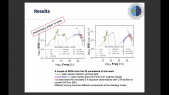
'Despite over 50 years of observations of Gamma-Ray Bursts (GRBs) many open questions remain about their nature and their environments in which the emission takes place. Polarization measurements of the GRB prompt emission have long been theorized to be able to answer most of these questions. The POLAR detector was a dedicated GRB polarimeter developed by a Swiss, Chinese and Polish collaboration. The instrument was launched, together with the second Chinese Space Lab, the Tiangong-2, in September 2016 after which it took 6 months of scientific data. During this period POLAR detected 55 GRBs as well as several pulsars. From the analysis of the GRB polarization catalog we see that the prompt emission is lowly or fully unpolarized. There is, however, the caveat that within single pulses there are strong hints of an evolving polarization angle which washes out the polarization degree in the time integrated analysis. Although the POLAR results thereby exclude a large portion of the polarization parameter space, to fully probe GRB polarization a significantly more sensitive detector is required. Such a detector, called POLAR-2, was recently approved for launch in 2024 and is currently being developed by a Swiss, Chinese, Polish and German collaboration. Here we will present a full overview of the POLAR mission and all its scientific measurement results. Additionally, we will present a short overview of the follow-up mission: POLAR-2, and how it will answer some of the questions raised by the POLAR results.'
Authors: Merlin Kole | For the POLAR and POLAR-2 Collaboration
Collaboration: POLAR and POLAR-2
Indico-ID: 189
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/600
Merlin Kole