BlaVar: A numerical study of long-term multi-wavelength blazar variability
-
135 views
-
7 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 7, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 15. July 2021 - 12:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/98542982538
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 98542982538
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/49-Studying-the-variable-emission-from-AGN-in-a-multi-wavelength-context-GAD-GAI-MM/119
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-04/5
Abstract:
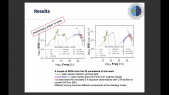
'Blazars are characterized by flux variability that is frequency-dependent and manifests in a variety of timescales. Decade-long monitoring of blazars at optical and infrared (OIR) wavelengths with the Small and Moderate Aperture Research Telescope System (SMARTS) in Chile and in gamma-rays with the Fermi Large Area Telescope (LAT) has enabled the systematic study of their multi-wavelength long-term variability. These studies pinpoint that besides extreme short-term variability (minutes to hours), a source can exhibit correlated and uncorrelated inter-band flux variability between different observation periods and/or on different timescales (days to years).rnrnIn this work, we investigate from a theoretical perspective the long-term variability properties of blazar emission. To do so, we impose variations on the main parameters of the one-zone leptonic model (injection luminosity of relativistic electrons, strength of magnetic field, Doppler factor, and external photon field luminosity) motivated by the Fermi-LAT full-mission light curves of blazars. Using as case studies two bright and well-monitored blazars from the SMARTS sample (PKS2155-304 and 3C273), we compute 10 year-long OIR, X-ray, and gamma-ray model light curves for different varying parameters. We compare the findings of our theoretical investigation with multi-wavelength observations using various measures of variability. While no single-varying parameter simulation can explain all multi-wavelength variability properties, our results motivate future time-dependent studies with coupling between two or more physical parameters to describe the multi-wavelength long-term blazar variability.'
Authors: Markos Polkas
Co-Authors: Maria Petropoulou Petropoulou | Georgios Vasilopoulos | Apostolos Mastichiadis | Megan Urry | Paolo Coppi | Charles Bailyn
Indico-ID: 759
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/680
Markos Polkas