Classification of Fermi-LAT sources with deep learning
-
126 views
-
4 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 4, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 13. July 2021 - 12:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/98542982538
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 98542982538
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/52-Analysis-Methods-Catalogues-Community-Tools-Machine-Learning-GAD-GAI/64
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-04/5
Abstract:
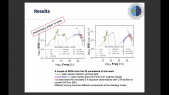
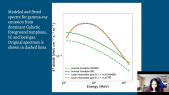
'Machine learning techniques are powerful tools for the classification of unidentified gamma-ray sources. We present a new approach based on dense and recurrent deep neural networks to classify unidentified or unassociated gamma-ray sources in the last release of the Fermi-LAT catalog (4FGL-DR2). Our method uses the actual measurements of the photon energy spectrum and time series as input for the classification, instead of specific, hand-crafted features. We focus on different classification tasks: the separation between extragalactic sources, i.e. Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN), and Galactic pulsars, the further classification of pulsars into young and millisecond pulsars and the sub-classification of AGN into different types. Since our method is very flexible, we generalize it to include multiwavelength data on the energy and time spectra coming from different observatories, as well as to account for uncertainties in the measurements and in the predicted classes. Our list of high-confidence candidate sources labelled by the neural networks provides targets for further multiwavelength observations to identify their nature, as well as for population studies.'
Authors: Silvia Manconi
Co-Authors: Michael Kraemer | Anja Butter | Thorben Finke | Felicitas Keil
Indico-ID: 1365
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/664
Silvia Manconi