A Data-Driven approach for the measurement of $^{10}$Be/$^9$Be flux ratio in Cosmic Ray with magnetic spectrometers
-
45 views
-
0 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 5, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 16. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://icrc2021.desy.de/pf_access_abstracts
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/Presenter-Forum-1-Evening-All-Categories/48
Abstract:
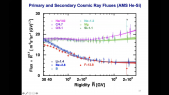
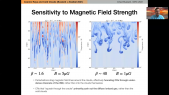
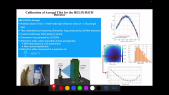
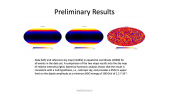
'Cosmic Rays (CR) are a powerful tool for the investigation of the structure of the magnetic fields in the galactic halo and the property of the Inter-Stellar Medium.rnTwo parameters of the Cosmic Ray propagation models: the galactic halo thickness, H, and the diffusion coefficient, D, are loosely constrained by current CR flux measurements, in particular a large degeneracy exists being only H/D well measured.rnThe $^{10}$Be/$^9$Be isotopic flux ratio (thanks to the 2 My lifetime of $^{10}Be$) can be used as a radioactive clock providing the measurement of CR residence time in the galaxy. This is an important tool to solve the H/D degeneracy. rnPast measurements of $^{10}$Be/$^9$Be isotopic flux ratio in CR are scarce, limited to low energy and affected by large uncertainties. Here a new technique to measure $^{10}$Be/$^9$Be isotopic flux ratio with a Data-Driven approach in magnetic spectrometers is presented. rnAs an example by applying the method to Beryllium data collected and published by PAMELA collaboration it is now possible to determine this important measurement avoiding the prohibitive uncertainties coming from the Monte Carlo simulation. It is shown that the accuracy of PAMELA data permits to infer a value of the halo thickness H within 25% precision.'
Authors: Francesco Nozzoli | Cinzia Cernetti
Indico-ID: 95
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/138
Francesco Nozzoli