Simulations and background estimates for the DAMIC-M experiment
-
57 views
-
2 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 2, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 13. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 96969970711
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/42-Direct-Dark-Matter-Present-and-Future-DM/86
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-07/8
Abstract:
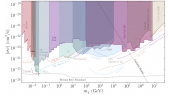
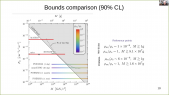
'DAMIC-M (Dark Matter in CCDs at Modane) is a near-future experiment aiming to search for low-mass dark matter particles through their interactions with silicon atoms in the bulk of charge-coupled devices (CCDs). This technique was pioneered by the DAMIC experiment at SNOLAB. Its successor DAMIC-M will have a 25 times larger detector mass and will employ a novel CCD technology (skipper amplifiers) which allows to achieve a readout noise of 0.07 e-. With these novelties, DAMIC-M will reach unprecedented sensitivities to dark matter candidates of the so-called hidden sector. A challenging requirement is the control of the radiogenic background at the level of a fraction of events per keV per kg-day of target exposure. Accurate Geant4 simulations are being employed to optimise the detector design and drive the material selection and handling. This poster provides a comprehensive overview of the explored detector designs, the estimated background, and the strategies for its mitigation.'
Authors: Claudia De Dominicis | Mariangela Settimo | For the DAMIC-M Collaboration
Collaboration: DAMIC-M
Indico-ID: 1196
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/553
Claudia De Dominicis