Properties of Neon, Magnesium, and Silicon Primary Cosmic Rays Results from the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer
-
87 views
-
2 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 4, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 14. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/91896950007
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 91896950007
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/17-Nuclear-CR-spectra-theory-and-observations-CRD/115
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-06/7
Abstract:
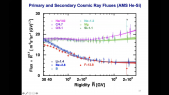
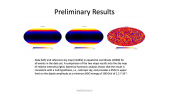
'We report the observation of new properties of primary cosmic rays, neon (Ne), magnesium (Mg), and silicon (Si), measured in the rigidity range 2.15 GV to 3.0 TV with 1.8 million Ne, 2.2 million Mg, and 1.6 million Si nuclei collected by the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer experiment on the International Space Station. The Ne and Mg spectra have identical rigidity dependence above 3.65 GV. The three spectra have identical rigidity dependence above 86.5 GV, deviate from a single power-law above 200 GV, and harden in an identical way. Unexpectedly, above 86.5 GV the rigidity dependence of primary cosmic rays Ne, Mg, and Si spectra is different from the rigidity dependence of primary cosmic rays He, C, and O. This shows that the Ne, Mg, and Si and He, C, and O are two different classes of primary cosmic rays.'
Authors: Alberto Oliva
Collaboration: AMS
Indico-ID: 763
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/107
Alberto Oliva