Constraining positron emission from pulsars with AMS-02 data
-
86 views
-
1 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 2, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 15. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://desy.zoom.us/j/91896950007
ZOOM-Meeting ID: 91896950007
ZOOM-Meeting Passcode: ICRC2021
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/16-Cosmic-Ray-Antiparticles-and-Electrons-CRD-DM-GAD-MM/128
Live-Stream URL: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/livestream/Discussion-06/7
Abstract:
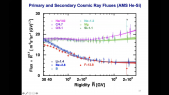
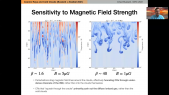
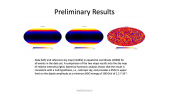
'The cosmic-ray flux of positrons is measured with high precision by the space-borne particle spectrometers AMS-02. The hypothesis that pulsar wind nebulae (PWNe) can significantly contribute to the excess of the positron ($e^+$) cosmic-ray flux has been consolidated after the observation of a $gamma$-ray emission at TeV energies of a few degree size around Geminga and Monogem PWNe. In this work we simulate pulsars populations adopting different distributions for the position in the Galaxy, the age, the spin-down period and the surface magnetic field of the sources, to overcome the incompleteness of the ATNF catalogue. We fit the AMS-02 data with the positron flux produced by these simulated populations, in order to understand the characteristics of the sources and to test different configurations of our Galaxy. The attempt of obtaining information about PWNe from the analysis of the AMS-02 $e^+$ data, which facilitate the search for point sources or new physics with respect to the matter component, has never been performed with this level of accuracy.'
Authors: Luca Orusa
Co-Authors: MATTIA DI MAURO | Silvia Manconi | Fiorenza Donato
Indico-ID: 198
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/149
Luca Orusa