Search for TeV decaying dark matter from the Virgo cluster of galaxies
-
63 views
-
2 likes
-
0 favorites
- uploaded July 3, 2021
Discussion timeslot (ZOOM-Meeting): 16. July 2021 - 18:00
ZOOM-Meeting URL: https://icrc2021.desy.de/pf_access_abstracts
Corresponding Session: https://icrc2021-venue.desy.de/channel/Presenter-Forum-1-Evening-All-Categories/48
Abstract:
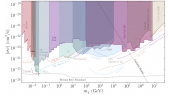
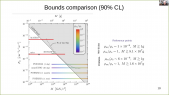
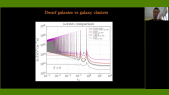
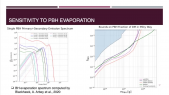
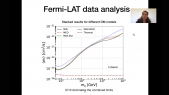
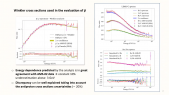
"Galaxy clusters' dynamics constitute a major piece of evidence for the existence of dark matter in astrophysical structures. The decay or annihilation of dark matter particles is hypothesized to produce a steady flux of very-high-energy gamma rays correlated with the direction of a cluster of galaxies. The Virgo cluster, being only ~16 Mpc away and spanning several degrees across the sky is an excellent target to search for signatures of particle dark matter interactions. The High Altitude Water Cherenkov (HAWC) observatory, due to its wide field of view and sensitivity to gamma rays at an energy-scale of 300 GeV—100 TeV is well-suited to perform the aforementioned search. We perform a search from the Virgo cluster for gamma-ray emission, assuming various dark matter sub-structure models using 1323 days of HAWC data. Our results provide the strongest constraints on the decay life-time of dark matter for masses above 10 TeV."
Authors: Mehr Nisa | Pat Harding for the HAWC Collaboration
Collaboration: HAWC
Indico-ID: 689
Proceeding URL: https://pos.sissa.it/395/530
Mehr Nisa